Page 66 - 22-0424
P. 66
The International Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand
Volume XI - 2019
the injury-induced tubular lesions, renal cell apoptosis and normalized the injury
induced renal dysfunction. One of the potential therapies of histone modification
is histone deacetylases inhibitor, such as vorinostat, causing renoprotective effects
(Liu et al., 2018; Zacharias et al., 2011). Several potential therapies of epigenetic
modifiers were shown in Figure 3.
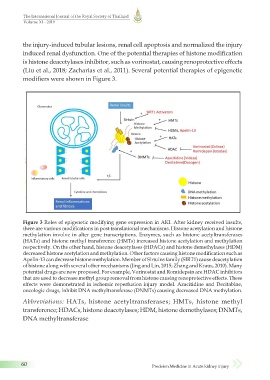
Figure 3 Roles of epigenetic modifying gene expression in AKI. After kidney received insults,
there are various modifications in post translational mechanisms. Histone acetylation and histone
methylation involve in alter gene transcriptions. Enzymes, such as histone acetyltransferases
(HATs) and histone methyl transference (HMTs) increased histone acetylation and methylation
respectively. On the other hand, histone deacetylases (HDACs) and histone demethylases (HDM)
decreased histone acetylation and methylation. Other factors causing histone modification such as
Apelin-13 can decrease histone methylation. Member of Sirtuins family (SIRT1) cause deacetylation
of histone along with several other mechanisms (Jing and Lin, 2015; Zhang and Kraus, 2010). Many
potential drugs are now proposed. For example, Vorinostat and Romidepsin are HDAC inhibitors
that are used to decrease methyl group removal from histone causing renoprotective effects. These
effects were demonstrated in ischemic reperfusion injury model. Azacitidine and Decitabine,
oncologic drugs, inhibit DNA methyltransferase (DNMTs) causing decreased DNA methylation.
Abbreviations: HATs, histone acetyltransferases; HMTs, histone methyl
transference; HDACs, histone deacetylases; HDM, histone demethylases; DNMTs,
DNA methyltransferase
60 Precision Medicine in Acute kidney injury
11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 60 11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 60