Page 62 - 22-0424
P. 62
The International Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand
Volume XI - 2019
Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is defined as an abrupt declining in kidney
function, which encompasses both structural damage and loss of functions (Makris
and Spanou, 2016). Diagnosis criteria of AKI from Kidney Disease Improving
Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guideline 2012 comprised of serum creatinine criteria
and decreased urine output criteria (Khwaja, 2012). In this guideline, AKI was
divided into 3 stages ranked by severity (Table1).
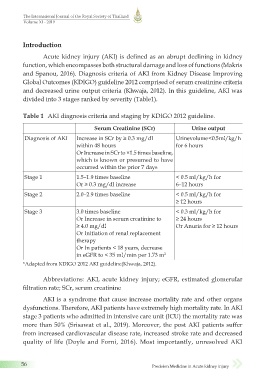
Table 1 AKI diagnosis criteria and staging by KDIGO 2012 guideline.
Serum Creatinine (SCr) Urine output
Diagnosis of AKI Increase in SCr by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl Urine volume < 0.5 ml/kg/h
within 48 hours for 6 hours
Or Increase in SCr to ×1.5 times baseline,
which is known or presumed to have
occurred within the prior 7 days
Stage 1 1.5–1.9 times baseline < 0.5 ml/kg/h for
Or ≥ 0.3 mg/dl increase 6–12 hours
Stage 2 2.0–2.9 times baseline < 0.5 ml/kg/h for
≥ 12 hours
Stage 3 3.0 times baseline < 0.3 ml/kg/h for
Or Increase in serum creatinine to ≥ 24 hours
≥ 4.0 mg/dl Or Anuria for ≥ 12 hours
Or Initiation of renal replacement
therapy
Or In patients < 18 years, decrease
in eGFR to < 35 ml/min per 1.73 m 2
*Adapted from KDIGO 2012 AKI guideline(Khwaja, 2012).
Abbreviations: AKI, acute kidney injury; eGFR, estimated glomerular
filtration rate; SCr, serum creatinine
AKI is a syndrome that cause increase mortality rate and other organs
dysfunctions. Therefore, AKI patients have extremely high mortality rate. In AKI
stage 3 patients who admitted in intensive care unit (ICU) the mortality rate was
more than 50% (Srisawat et al., 2019). Moreover, the post AKI patients suffer
from increased cardiovascular disease rate, increased stroke rate and decreased
quality of life (Doyle and Forni, 2016). Most importantly, unresolved AKI
56 Precision Medicine in Acute kidney injury
11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 56 11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 56