Page 64 - 22-0424
P. 64
The International Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand
Volume XI - 2019
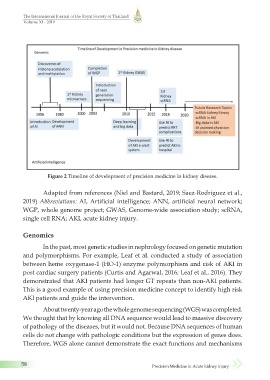
Figure 2 Timeline of development of precision medicine in kidney disease.
Adapted from references (Niel and Bastard, 2019; Saez-Rodriguez et al.,
2019) Abbreviations: AI, Artificial intelligence; ANN, artificial neural network;
WGP, whole genome project; GWAS, Genome-wide association study; scRNA,
single cell RNA; AKI, acute kidney injury.
Genomics
In the past, most genetic studies in nephrology focused on genetic mutation
and polymorphisms. For example, Leaf et al. conducted a study of association
between heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) enzyme polymorphism and risk of AKI in
post cardiac surgery patients (Curtis and Agarwal, 2016; Leaf et al., 2016). They
demonstrated that AKI patients had longer GT repeats than non-AKI patients.
This is a good example of using precision medicine concept to identify high risk
AKI patients and guide the intervention.
About twenty-year ago the whole genome sequencing (WGS) was completed.
We thought that by knowing all DNA sequence would lead to massive discovery
of pathology of the diseases, but it would not. Because DNA sequences of human
cells do not change with pathologic conditions but the expression of genes does.
Therefore, WGS alone cannot demonstrate the exact functions and mechanisms
58 Precision Medicine in Acute kidney injury
11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 58 11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 58