Page 84 - The lraternational Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand.indd
P. 84
The International Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand
Volume XV-2023
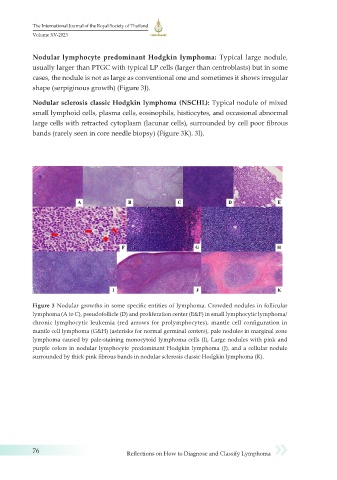
Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: Typical large nodule,
usually larger than PTGC with typical LP cells (larger than centroblasts) but in some
cases, the nodule is not as large as conventional one and sometimes it shows irregular
shape (serpiginous growth) (Figure 3J).
Nodular sclerosis classic Hodgkin lymphoma (NSCHL): Typical nodule of mixed
small lymphoid cells, plasma cells, eosinophils, histiocytes, and occasional abnormal
large cells with retracted cytoplasm (lacunar cells), surrounded by cell poor fibrous
bands (rarely seen in core needle biopsy) (Figure 3K). 3I).
Figure 3 Nodular growths in some specific entities of lymphoma. Crowded nodules in follicular
lymphoma (A to C), pseudofollicle (D) and proliferation center (E&F) in small lymphocytic lymphoma/
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (red arrows for prolymphocytes), mantle cell configuration in
mantle cell lymphoma (G&H) (asterisks for normal germinal centers), pale nodules in marginal zone
lymphoma caused by pale-staining monocytoid lymphoma cells (I), Large nodules with pink and
purple colors in nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (J), and a cellular nodule
surrounded by thick pink fibrous bands in nodular sclerosis classic Hodgkin lymphoma (K).
76 Reflections on How to Diagnose and Classify Lymphoma