Page 87 - 22-0424
P. 87
The International Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand
Volume XI - 2019
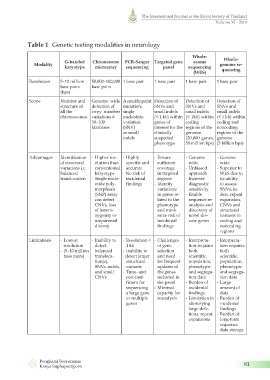
Table 1 Genetic testing modalities in neurology
Whole-
G-banded Chromosome PCR-Sanger Targeted gene exome Whole-
Modality genome se-
karyotype microarray sequencing panel sequencing
(WES) quencing
Resolution 5–10 million 50,000–100,000 1 base pair 1 base pair 1 base pair 1 base pair
base pairs base pairs
(bps)
Scope Number and Genome wide A specific point Detection of Detection of Detection of
structure of detection of mutation; SNVs and SNVs and SNVs and
all the copy number single small indels small indels small indels
chromosomes variations ≥ nucleotide (< 1 kb) within (< 1kb) within (< 1 kb) within
50–100 variation genes of coding coding and
kilobases (SNV) interest for the regions of the noncoding
or small clinically genome regions of the
indels suspected (20,000 genes, genome
phenotype 50 million bps) (3 billion bps)
Advantages Identification - Higher res- - Highly - Ensure - Genome - Genome
of structural olution than specific and sufficient wide wide
variations i.e. conventional accurate coverage - Unbiased - Superior to
balanced karyotype - No risk of in targeted approach WES due to
translocation - Single nucle- incidental regions - Increase its ability
otide poly- findings - Identify diagnostic to assess
morphism variations sensitivity SNVs, in-
(SNP) array in genes re- - Enable dels, repeat
can detect lated to the sequence re- expansion,
CNVs, loss phenotype analysis and CNVs and
of hetero- and mini- discovery of structural
zygosity or mize risk of novel dis- variants in
uniparental incidental ease genes coding and
disomy findings noncoding
regions
Limitations - Lowest - Inability to - Resolution < - Challenges - Interpreta- - Interpreta-
resolution detect 1 kb of gene tion requires tion requires
- (5–10 million balanced - Inability to selection both both
base pairs) transloca- detect larger and need scientific, scientific,
tion(s), structural for frequent population, population,
SNVs, indels, variants updates of phenotypic phenotypic
and small - Time- and the genes and segrega- and segrega-
CNVs cost-inef- included in tion data tion data
ficient for the panel - Burden of - Large
sequencing - Minimal incidental amount of
a large gene capacity for findings data
or multiple reanalysis - Limitation in - Burden of
genes identifying incidental
large dele- findings
tions, repeat - Burden of
expansions long-term
sequence
data storage
Ponghatai Boonsimma
Kanya Suphapeetiporn 81
11/7/2565 BE 13:30
_22-0424(077-088)8.indd 81
_22-0424(077-088)8.indd 81 11/7/2565 BE 13:30