Page 72 - 22-0424
P. 72
The International Journal of the Royal Society of Thailand
Volume XI - 2019
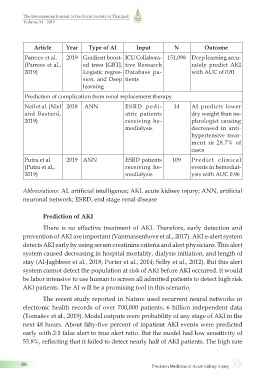
Article Year Type of AI Input N Outcome
Parreco et al. 2019 Gradient boost- ICU Collabora- 151,098 Deep learning accu-
(Parreco et al., ed trees [GBT], tive Research rately predict AKI
2019) Logistic regres- Database pa- with AUC of 0.81
sion, and Deep tients
learning
Prediction of complication from renal replacement therapy
Neil et al. (Niel 2018 ANN ESRD pedi- 14 AI predicts lower
and Bastard, atric patients dry weight than ne-
2019) receiving he- phrologist causing
modialysis decreased in anti-
hypertensive treat-
ment in 28.7% of
cases
Putra et al. 2019 ANN ESRD patients 109 Predict clinical
(Putra et al., receiving he- events in hemodial-
2019) modialysis ysis with AUC 0.96
Abbreviations: AI, artificial intelligence; AKI, acute kidney injury; ANN, artificial
neuronal network; ESRD, end stage renal disease
Prediction of AKI
There is no effective treatment of AKI. Therefore, early detection and
prevention of AKI are important (Vanmassenhove et al., 2017). AKI e-alert system
detects AKI early by using serum creatinine criteria and alert physicians. This alert
system caused decreasing in hospital mortality, dialysis initiation, and length of
stay (Al-Jaghbeer et al., 2018; Porter et al., 2014; Selby et al., 2012). But this alert
system cannot detect the population at risk of AKI before AKI occurred. It would
be labor intensive to use human to screen all admitted patients to detect high risk
AKI patients. The AI will be a promising tool in this scenario.
The recent study reported in Nature used recurrent neural networks in
electronic health records of over 700,000 patients, 6 billion independent data
(Tomašev et al., 2019). Model outputs were probability of any stage of AKI in the
next 48 hours. About fifty-five percent of inpatient AKI events were predicted
early with 2:1 false alert to true alert ratio. But the model had low sensitivity of
55.8%, reflecting that it failed to detect nearly half of AKI patients. The high rate
66 Precision Medicine in Acute kidney injury
11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 66 11/7/2565 BE 13:28
_22-0424(055-076)7.indd 66